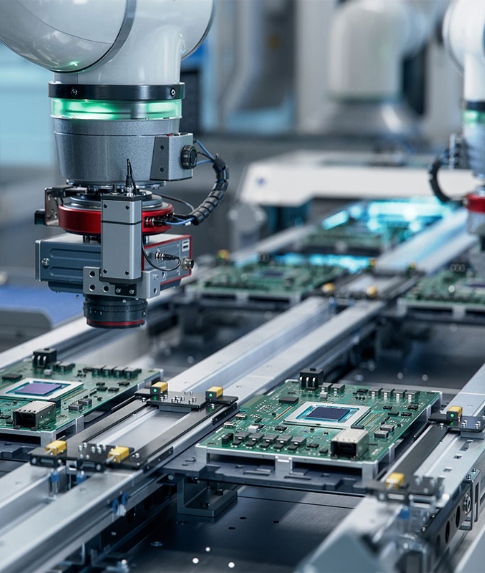


SMT Assembly (Surface Mount Technology Assembly) is a modern method used in electronics manufacturing to mount components directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs). This process is essential for producing compact, high-performance devices. Here's a detailed breakdown:
Key Steps in SMT Assembly:
1.Solder Paste Application:
A stencil aligns with the PCB, and solder paste (a mix of flux and tiny solder particles) is applied to pads where components will be placed. This is typically done using a screen-printing machine.
2.Component Placement:
Automated pick-and-place machines precisely position surface-mount devices (SMDs) like resistors, capacitors, and ICs onto the solder paste. These machines handle components ranging from tiny 01005 packages (0.4mm x 0.2mm) to larger BGAs.
3.Reflow Soldering:
The PCB passes through a reflow oven with a controlled temperature profile. The solder paste melts (reflow), forming reliable electrical connections as it cools. The profile includes preheat, thermal soak, reflow, and cooling stages to avoid defects.
4.Inspection and Testing:
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI): Checks for placement accuracy, solder defects (e.g., bridging, tombstoning), or missing components.
5.X-Ray Inspection: Examines hidden joints under components like BGAs.
6.Functional Testing: Ensures the PCB operates as intended.
7.Secondary Processes (if needed):
8.Double-Sided Assembly: Repeat the process for the PCB’s other side.
9.Conformal Coating: Protects against environmental factors.
10.Through-Hole Integration: For mixed-technology boards.

Advantages of SMT:
Challenges:
Applications:
Environmental Considerations:
Lead-free solder (RoHS-compliant) is standard, reducing environmental impact.
SMT Assembly is the backbone of modern electronics, balancing efficiency, precision, and scalability to meet the demands of today’s compact, high-tech devices.
Our hours
24H