A Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is a foundational component in modern electronics, serving as the physical platform that mechanically supports and electrically connects electronic components using conductive pathways etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate.
Below is a detailed breakdown of its key aspects:
1. Structure and Composition
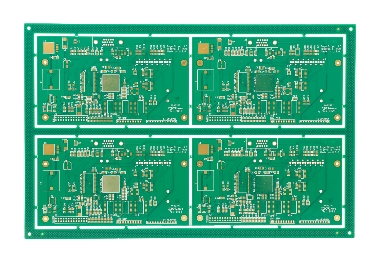
- Layered Design: PCBs can be single-sided (components on one side, wiring on the other), double-sided (conductive layers on both sides connected by vias), or multilayered (e.g., 4–100 layers), with each layer separated by insulating material.
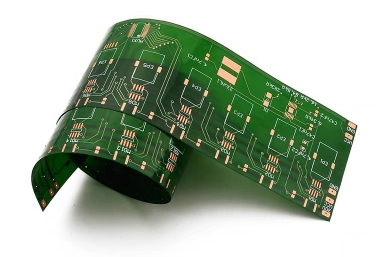
- Materials: Common substrates include rigid materials like epoxy resin (for rigid PCBs) or flexible polymers like polyimide (for flexible PCBs). Copper is used for conductive traces, and a solder mask (green/brown coating) protects against oxidation and short circuits
2. Types of PCBs
- Rigid PCBs: Used in devices like computers and televisions, made from solid materials like fiberglass
- Flexible PCBs: Bendable boards for wearables, medical devices, or tight spaces
- Rigid-Flex PCBs: Combine rigid and flexible layers, ideal for aerospace and military applications
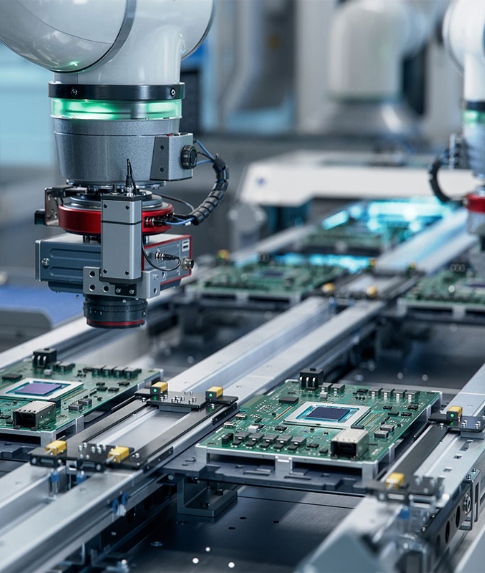
3. Core Functions
- Electrical Connectivity: Routes signals between components (e.g., resistors, ICs)
- Mechanical Support: Holds components in place and withstands environmental stress
- Signal Integrity: Manages impedance and reduces electromagnetic interference (EMI) in high-speed circuits
4. Applications
PCBs are ubiquitous in electronics, including:
- Consumer devices (smartphones, laptops)
- Industrial systems (robotics, power supplies)
- Automotive and aerospace systems (engine controls, avionics)
- Medical equipment (imaging devices, monitors)
5. Historical Context
Invented by Paul Eisler in 1936, PCBs gained prominence in military radios during WWII and became commercialized in 1948. Their evolution enabled miniaturization and reliability in electronics
Key Features
- Design Complexity: Modern PCBs use CAD tools for high-density layouts, adhering to standards like IPC-2221
- Manufacturing: Involves etching, drilling, plating, and testing, with challenges in precision and yield
For instance, a smartphone’s motherboard is a multilayer PCB integrating processors, memory, and sensors, while a simple thermostat might use a single-sided board.The PCB’s role as the “mother of electronics” underscores its irreplaceability in technological advancement.
Welcome to consult our sales engineer with BOM list and Gerber file